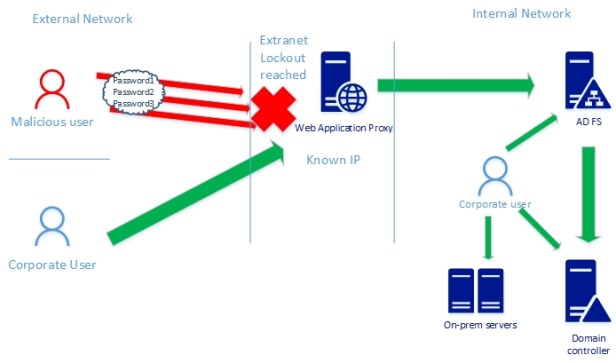
Attacks against identity and access systems like AD FS are quite common nowadays. Feature called Extranet Account Lockout was introduced in Windows Server 2012 R2 to prevent attacks these kinds of attacks. When in use, AD FS will stop sending authentication requests to domain controller from an external network when a threshold is reached.
AD FS Smart Lockout (ESL) is a new feature in Windows Server 2016 introduced originally in March cumulative update but postponed due to technical issues to June. It prevents Denial of Service attacks without locking on-premises Active Directory account (like password spray – trying the same password on all user accounts and brute-force attacks – trying multiple passwords for one user account.
What’s the Difference with “Extranet Account Lockout” and “Smart Lockout”?
The main differences are:
- Usage of AccountActivity table in ESL
- ESL works only with W2016 AD FS
- In Extranet Account Lockout incoming authentications are handled inside same counter and service doesn’t keep track familiar locations and malicious IPs.
The Extranet Smart Lockout (ESL) enables AD FS to differentiate between sign-in attempts with a usage of AccountActivity table in AD FS database. As a result, AD FS can lock out attackers while letting valid users continue to use their accounts which helps to prevent denial-of-service on the user and protects against targeted attacks.
Key features in Smart Lockout (from docs.microsoft.com)
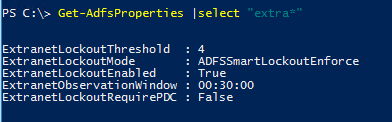
- When authentication is successful, client IP-address is saved as familiar locations to artifact database table called “AccountActivity” in ADFS.
- If password-based authentication fails and the credentials do not come from a familiar location, the failed authentication count is incremented.
- After the number of failed password attempts from unfamiliar locations reaches the lockout threshold, if password-based authentication from an unfamiliar location fails, the account is locked out.
- Users who are coming from familiar location doesn’t experience any lockouts because familiar lockouts are handled with separate counter.
Configuration options for Extranet Smart Lockout (ESL)
- ADPasswordCounter – Legacy AD FS “Extranet Soft Lockout” mode, which does not differentiate based on location and is default mode in W2016 ADFS
- ADFSSmartLockoutLogOnly – Extranet Smart Lockout, logging mode
- ADFSSmartLockoutEnforce – Extranet Smart Lockout, enforced mode
Enabling Smart Lockout
Before making any configurations installation of June update rollup is needed (KB4284880) is needed to all farm AD FS instances.
Recommendation is to configure ADFS Smart Lockout to logging mode for a couple of days to make sure that your configuration is working as expected. I have let this service run in logging mode for one (1) week before changing it to enforce mode. Following commands in PowerShell are needed to configure necessary settings.
Configure Extranet Lockout
#Configure permissions to new AccountActivity table in ADFS Artifact store (ADFS administrator credentials are needed)
- $cred = Get-Credential
- Update-AdfsArtifactDatabasePermission -Credential $cred
#ADFS Auditing Enabled
- From local group policy editor or by local group policy editor
- computer configuration – Windows settings – security settings – advanced audit policy – system audit policies (local) – object access – application generated – success & failure
- auditpol.exe /set /subcategory:”Application Generated” /failure:enable /success:enable
- Set-ADFSProperties -LogLevel Verbose,Errors,Warnings,Information
#Set lockout threshold, observation window and enable lockout(these values needs to mapped to AD DS password policy to avoid account lockout in AD DS)
- Set-AdfsProperties -ExtranetLockoutThreshold 4
- Set-AdfsProperties -ExtranetObservationWindow ( new-timespan -minutes 15 )
- Set-AdfsProperties -EnableExtranetLockout $true
#Set Smart Lockout loggin mode
- Set-AdfsProperties -ExtranetLockoutMode AdfsSmartlockoutLogOnly
- Restart-Service adfssrv
#When ready to change to enforce mode run this command
- Set-AdfsProperties -ExtranetLockoutMode AdfsSmartLockoutEnforce
How it looks in action?
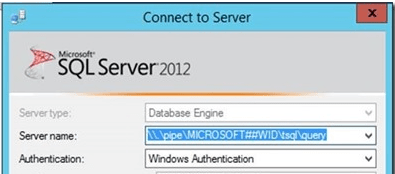
When launching SQL Management Studio and connecting to WID database add this string to the server name field: \\.\pipe\MICROSOFT##WID\tsql\query
Configuring permissions

AccountActivity table where information of known IPs are saved

Extranet Account Lockout settings in Enforced mode. These values need to be mapped to on-premises Active Directory password policy instructed in Extranet Account Lockout configuration guidance.
If the user hasn’t logged to ADFS or service has just been started there isn’t nothing to show in the database

After multiple failures, my account has been locked out from unknown IPs but the user is able to login from familiar IPs

Naturally account stays active at on-premises Active Directory

Finally, the AccountActivity table where information is actually stored.

Summary
Lately extremely valuable features has been published around Hybrid Identity security like Extranet Smart Lockout, Extranet Banned IPs and Azure AD Password Protection for Windows Server Active Directory. First two would be the main reasons for upgrade your AD FS farm to W2016 level. By configuring ADFS Smart Lockout you keep your users connected and productive at internal network even case of attack.

Thank you so much for this article! It is so hard to find information on this topic. In this sentence:
“If user hasn’t logged to ADFS or service has just been started there isn’t nothing to show in database”
you discuss how if the ADFS service is restarted that the database doesn’t know the person when they log in. Why is the database getting cleared on restart and can this be changed?
Also, when you use the SQL Management studio to look at the database what is the “server name” that you are using?
Thanks again! Great article.
Hi, glad you liked it! Database clearance was own finding during a test phase. I currently don’t have answers for you why wid database is cleared on service restart and can it be changed, I’ll try to find it anyway from my network.
The second question was about the server name (I can add this one to blog also) when you launch SQL Management studio add this to server name field: “\\.\pipe\MICROSOFT##WID\tsql\query”. Then connection should work fine.
Thanks,
Sami
Thanks for the quick reply. I’ll try that server name.
Hi again,
I used the server name that you providde below. When I look in the WID database I do not see Artifactstore.AccountActivity Table. What actually creates it? I can use the get-adfsaccountactivity and it works and it looks like the ESL is working.
Is it possible that it is working without the AccountActivity table being created?
Thanks,
Kelly
Hi Kelly,
Artifactstore.AccountActivity table should definitely be there because that’s the place where known ip’s are saved. Have you logged in with a user account who has permissions to all the tables? My own environment is currently unusable I cannot double check this right now. When you run the command below table is created.
$cred = Get-Credential
Update-AdfsArtifactDatabasePermission -Credential $cred
If you need help with troubleshooting this one we can continue a discussion via email.
Thanks,
Sami
Thanks Sam. Iâm on a support call with MS now. Iâll let you know what I find out.
Hi,
Just got off the phone with Microsoft. It was a rights issue with creating the AccountActivity table in the database. We went into ADFS manager and gave the admin account that we were using explicit rights to update the table. “Enable delegation for service authentication”. We added the domain admins group. Rebooted the server and the table appeared.
Also, when I restart the service the data stays stored in the table. It is not getting wiped out now.
Thanks,
Kelly
Hi,
Glad that you got it working and visibility to created table. Thanks a lot for the information. Extremely good info that data on the table is not wiped out when service is restarted. Anyway, that was behavior in my environment every time after restart. I’ll update the blog regarding data retention part after I have tested it in own environment. Thanks again!
BR,
Sami
Hello.
Thanks for your article.
I did setup ESL in LogOnly mode, but there seems to be something wrong.
Shouldn’t the database tables “ArticfactStore.AccountActivity” and “ArtifactStore.Artifacts” already get filled with data in LogOnly mode?
Hello Frank,
And sorry for late reply. I assume that those definitely should, otherwise you wouldn’t benefit from audit mode quite much. Have you been able to find solution for this already? I need to verify functionality in my test environment.
Hi Frank,
Did you ever figure this out? I seem to be having the same problem where the tables are there but no data in them.
Hello,
There has been two question in this conversation
1. Does table contain data if ADFS service is restarted?
– In my environment If I restart ADFS service there isn’t nothing in my database table. All patches are installed but situation still remains same.
2. In logging only mode, are table filled with entries?
– If service is in logging only mode entries are filled to database
ESL is good, but it does not prevent the lock of all accounts of the company
And what you suggest to avoid that ?
Very good blog. Thank you.
Glad you liked it:)
First off – really nice to see this blog 🙂
We have just turned on Extranet lockout in logonly mode. Our test env is 2 WAP and 2 ADFS servers running on SQL with DAGs. We see the accountactivity table and it has data. When we try to query the data using get-adfsaccountactivity it throws a “userActivityRestServiceException” error.
We see even 561 in the ADFS event log – Authorization failed when connecting to the account store endpoint on server
We are running the command directly on the ADFS server.
Just wondered if this rings any bells? :_ thank you
Hello Jack!
Thank you for the kind words:)
I faced the same error in my environment if the user wasn’t authenticated and I tried to query information from the SQL database.
– Have you verified that the user has been logged through ADFS before making a query?
– You said that you can see the data, is the data from the user which you were trying to find with powershell?
– Does this same behavior happen with every user or only with some?
– Have you tried get-adfsaccountactivity with -Server switch?
Please let me know does any of these help and I can make further testing in my test environment.
Thanks,
Sami
Thanks Sami for the insights.
Do you have any update on the userActivityRestServiceException and Event 561? We experiencing the same issue on Windows 2016, and I didn’t find any solution yet.
Hi Benjamin, no updates compared to the info above. I faced the error when the user was not authenticated, not in any other scenario.
After lots of research and testing I found out that Get-AdfsAccountActivity internally makes a REST-Request to an url like that:
http://sts.contoso.com/adfs/users/user%40contoso.com?api-version=1
It uses the Authorization header and there it failed with http (401) Unauthorized
The Windows System log had this error: “The Kerberos client received a KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED error from the server SERVICE_ACCOUNT. The target name used was HTTP/sts.contoso.com. This indicates that the target server failed to decrypt the ticket provided by the client. This can occur when the target server principal name (SPN) is registered on an account other than the account the target service is using”
It was finally an issue by the server principal name (SPN). Years ago we had the current ADFS running on a temporary domain, because we replaced an older ADFS server. We changed the domain when we went to production. But the SPN was not updated. So I had to fix the SPN using setspn, as documented at https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/1427.ad-fs-2-0-how-to-configure-the-spn-serviceprincipalname-for-the-service-account.aspx. Interestingly that wrong configuration had no other negative impacts during the last years.
Finally Get-AdfsAccountActivity is working.
Hi Benjamin,
Thank you for the useful fix for the issue. Really appreciate your feedback! I will add a mention of your research to the blog.
Thank you ffor this